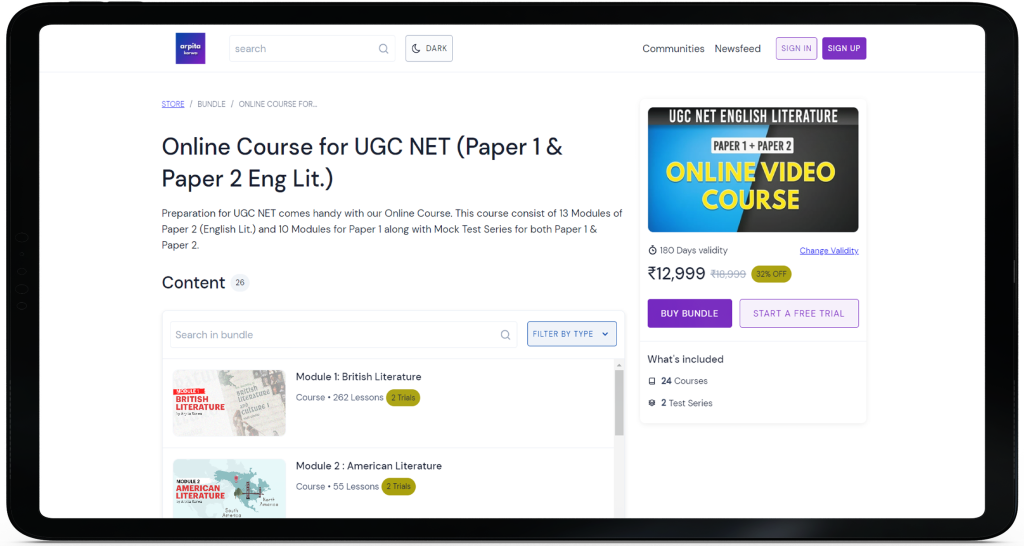
UGC NET Paper 1 December 2021 (Conducted on 25th December 2021 : Morning Shift)
October 18, 2022 2025-08-18 16:34UGC NET Paper 1 December 2021 (Conducted on 25th December 2021 : Morning Shift)
December 2021: Paper 1 (Conducted on 25th Dec 2021 : Morning Shift)
Q.1-5)
Q.1) Increase of expenditure from 2019 to 2020 in percentage is:
[1] 6.9
[2] 5.3
[3] 5.8
[4] 7.2
Correct Answer: 1
Q.2) In which year is the Travel expenditure (as a percentage) minimum?
[1] 2017
[2] 2018
[3] 2019
[4] 2020
Correct Answer: 3
Q.3) What s the average expenditure on Travel and Hospitality during 2016 to 2020?
[1] 110.5
[2] 109.4
[3] 108.3
[4] 108.7
Correct Answer: 2
Q.4) In which year is the ratio of Salary to Hospitality maximum?
[1] 2017
[2] 2018
[3] 2019
[4] 2020
Correct Answer: 2
Q.5) the difference between average expenditure on tax and average expenditure on loan interest;
[1] 54.8
[2] 55.6
[3] 56.4
[4] 57.2
Correct Answer: 3
Q.6) Match the column:
A. Reading/language arts
B. Mathematics
C. Science
D. Social Studies
I. Software programs to develop basic reading skills
II. Simulations to explore distant places and times
III. Graphica calculations to illustrate abstract or hard-to-visualize relationships
IV. Simulations to illustrate complex relationships
[1] A-II B-I C-III D-IV
[2] A-I B-III C-IV D-II
[3] A-III B-IV C-II D-I
[4] A-IV B-II C-I D-III
Correct Answer: 2
Q.7) Statement I: You can make the behaviours you teach, more authentic by changing the irrelevant aspects or context of what you are teaching as often as possible and in as many different ways as possible.
Statement II: To teach behaviour that is authentic, your lesson need not present content in a way in which it will be used by your learners on assessments, in subsequent grades, and in the world outside your classroom.
[1] Both Statement I and Statement Il are correct
[2] Both Statement I and Statement Il are incorrect
[3] Statement I is correct but Statement Il is incorrect
[4] Statement I is incorrect but Statement Il is correct
Correct Answer: 3
Q.8) Which of these decision traps pertains to thinking and planning activities?
A. NOT keeping records
B. Overconfidence
C. Plunging-in
D. Frame-blindness
E. Poor frame control
[1] A, B and C only
[2] B, C and D only
[3] A, C and E only
[4] C, D and E only
Correct Answer: 4
Q.9) Arrange these instructional events for delivering the lesson to students in sequential order from the beginning to the end.
A. Informing the learner of the objectives
B. Eliciting desired behaviour
C. Gaining attention
D. Presenting the content
E. Providing feedback
[1] A, D, B, C, E
[2] D, C, B, A, E
[3] C, A, D, B, E
[4] B, C, A, E, D
Correct Answer: 3
Q.10) Sometimes, subjects who know that they are in a control group may work hard to excel against the experimental group. Such a phenomenon is known as.
[1] Controlled Competition
[2] Motivational Contest
[3] Compensatory Rivalry
[4] Inspirational Influence
Correct Answer: 3
Q.11) Analytic Induction is a method of
A. Systematic interpretation of events
B. Generating hypothesis
C. Testing hypothesis
D. Freestyle interpretation
E. Testing null hypothesis only
[1] A, Band C only
[2] B, C and D only
[3] C, D and E only
[4] A, B and E only
Correct Answer: 1
Q.12) The characteristics of longitudinal studies are:
A. Limited results
B. Do not need heavy investment
C. Provide alternative choices
D. Allow insight into the time order of variables
E. Focuses on individual or institutional developments
[1] A, B and C only
[2] B, C and D only
[3] C, D and E only
[4] A, D and E only
Correct Answer: 3
Q.13) Assertion A: A research question should have some connection with an existing theory or research.
Reason R: The research question formulated should be either too broad or too narrow.
[1] Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
[2] Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
[3] A is true but R is false
[4] As false but R is true
Correct Answer: 3
Q.14) Match the column:
A. History
B. Maturation
C. Testing
D. Demand characteristics
I. Happens when subjects are given similar pre-tests and post-tests
II. Subjects’ reactions to experimental conditions
III. Occurace of various events during a study
IV. Biological and psychological characters changing during the course of the study
[1] A-I B-II V-III D-IV
[2] A-II B-III C-IV D-I
[3] A-III B-IV C-I D-II
[4] A-IV B-I C-II D-III
Correct Answer: 3
Q.15) Which of the following is considered unethical communication?
[1] Use of alternative source of information
[2] Not revealing the source of information
[3] Propaganda
[4] Non-commercial publicity
Q.16) Communication means _______ of information
A. Suppression
B. Exchange
C. Understanding
D. Contextualisation
E. Abstraction
[1] A, B and C only
[2] B, C and D only
[3] C, D and E only
[4] A, B and E only
Correct Answer: 2
Q.17) Which of the following are determinants in transactional communication?
A. Social context
B. Cultural context
C. Relational context
D. Legal context
E. Delayed context
[1] A, B and C only
[2] B, C and D only
[3] C, D and E only
[4] A, B and E only
Correct Answer: 1
Q.18) Statement I: In communication, language ambiguity takes place because of the incorrect use of words.
Statement II: Informal time terms lead to different interpretations.
[1] Both Statement I and Statement Il are correct
[2] Both Statement I and Statement Il are incorrect
[3] Statement I is correct but Statement Il s incorrect
[4] Statement I is incorrect but Statement Il s correct
Correct Answer: 1
Q.19) Match the column:
Concept of Power communication
A. Legitimate power
B. Referent power
C. Reward power
D. Expert power
Description of feature
I. Specialised knowledge
II. By virtue of position
III. When others feel to be like you
IV. Control over what others seek
[1] A-I B-II C-III D-IV
[2] A-III B-IV C-I D-II
[3] A-IV B-I C-II D-III
[4] A-II B-III C-IV D-I
Correct Answer: 4
Q.20) How many minutes is it before 12 noon if 48 minutes ago it was three times as many minutes past 9 AM?
[1] 33 minutes
[2] 43 minutes
[3] 40 minutes
[4] 43.5 minutes
Correct Answer: 1
Q.21) The population of a bacteria culture increases at a rate of 4% per annum. There is an additional increase of 1% of the population due to some reason. The percentage increase in the population after two years is, therefore
[1] 10
[2] 10.5
[3] 10.25
[4] 10.75
Correct Answer: 3
Q.22) Statement I: A number is divisible by 12 if the number is divisible by both 3 and 4.
Statement II: A number is divisible by 3, if and only if the sum of all the digits of the number is divisible by 6.
[1] Both Statement I and Statement Il are true
[2] Both Statement I and Statement Il are false
[3] Statement I is true but Statement Il is false
[4] Statement I is false but Statement Il is true
Correct Answer: 3
Q.23) Which of the following statement/s is/are correct?
A. Yaman crosses a 600m long road in 5 minutes. His speed is 7.2 km/hr
B. Vinod performs 2/15 of his total journey by train; 9/20 by bus and rest 10 km on cycle. His total journey is 24 km
C. Anita can complete a work in 8 days. She can complete 1/8 fraction of the work in two days
[1] A only
[2] B only
[3] A and B only
[4] A and C only
Correct Answer: 3
Q.24) Consider ‘E’ proposition as True and I as False in a square of opposition of proposition and pick the correct answer from the options given below
[1] ‘A’ is True; ‘A’ is True
[2] ‘O’ is False; ‘E’ is False
[3] ‘I’ is False; ‘E’ is True
[4] ‘O’ is Undetermined; ‘O’ is Undetermined
Correct Answer: 3
Q.25) Name the fallacy committed in the statements below
“All text books are books intended for careful study.
Some reference books are books intended for careful study.
Therefore, some reference books are text books.”
[1] Existential Fallacy
[2] Undistributed Middle
[3] Affirmative conclusion from Negative Premise
[4] Exclusive Premises
Correct Answer: 2
Q.26) ‘I see a piece of fragrant sandalwood’ would correctly represent
[1] Samanyalakshna
[2] Jianalakshana
[3] Yogaja
[4] Nirvikalpa Pratyaksa
Correct Answer: 2
Q.27) Which of the following is NOT a constituent-member of the Indian syllogistic argument?
[1] Upanaya
[2] Udaharana
[3] Sanshaya
[4] Hetu
Correct Answer: 3
Q.28) Which one of the following is a disadvantage of using proprietary software rather than open source software?
[1] Proprietary software can only be accessed with a password
[2] Proprietary software can only be used on proprietary systems
[3] Proprietary software is usually more expensive
[4] Proprietary software can only be used with an Internet connection
Correct Answer: 3
Q.29) Assertion A: VisiCalc, the first spreadsheet software application, is a commonly cited example of one of the first killer applications.
Reason R: VisiCalc helped in bringing PCs into the business realm.
[1] Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
[2] Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
[3] A is true but R is false
[4] A false but R is true
Correct Answer: 1
Q.30) Match the column:
A. Printed copies of instructions on how to play his music
B. Sound files of him playing his music
C. Video file of him playing his music
D. Images of the instruments he teaches
I. mp3
II. DOC
III. JPEG
IV. AVI
[1] A-III B-I C-IV D-II
[2] A-I B-II C-III D-IV
[3] A-II B-I C-IV D-III
[4] A-II B-I C-III D-IV
Correct Answer: 3
Q.31) Which of the following statements about internal and external computer memory are true?
A. A portable hard drive is an example of internal memory
B. Magnetic tape is used to store backups of data
C. RAM is an internal memory
D. ROM loses its data when the power is turned off
[1] A and B only
[2] A and C only
[3] C and D only
[4] B and C only
Correct Answer: 4
Q.32) Match the column:
A. Numerical ID for each device on the internet
B. Unique ID for a network interface card (NIC)
C. Use of the Internet to make phone calls
D. Text used by web browsers to locate a web address on the internet
I. VOIP
II. URL
III. MAC Address
IV. IP Address
[1] A-II B-III C-I D-IV
[2] A-IV B-III C-II D-I
[3] A-I B-III C-IV D-II
[4] A-IV B-III C-I D-II
Correct Answer: 4
Q.33) Identify the correct sequence of BRICS countries in relation to their Sustainable Development Goals Index (from highest to lowest) as per the Sustainable Development Report (2020)
A. China
B. India
C. South Africa
D. Brazil
E. Russian Federation
[1] C > D > E > A > B
[2] E > D > C > A > B
[3] C > E > B > D > A
[4] A > D > E > C > B
Correct Answer: 4
Q.34) Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol envisages reduction in HFCs consumption by late 2040s to the extent of
[1] 50-55%
[2] 65-70%
[3] 80-85%
[4] 90-95%
Correct Answer: 3
Q.35) According to Red list, the percentage of threatened mammals in the world is about
[1] 20%
[2] 25%
[3] 40%
[4] 45%
Correct Answer: 2
Q.36) The permissible limit for Arsenic in drinking water, as per Indian Standards [IS:10500] is
[1] 0.05 mg/L
[2] 0.5 mg/L
[3] 1.0 mg/L
[4] 2.0 mg/L
Correct Answer: 1
Q.37) From the energy security perspective, which of the following energy sources is considered most secure for India?
[1] Geothermal
[2] Solar
[3] Wind
[4] Hydro
Correct Answer: 2
Q.38) Which of the following are ‘deemed to be university’?
A. NCERT
B. NIEPA
C. Jamia Hamdard
D. Jamia Millia Islamia
E. IIIT
[1] A and B only
[2] B and C only
[3] C and D only
[4] D and E only
Correct Answer: 2
Q.39) The NEP-2020 recommends that the duration of the B.Ed. programme will be of
A. One year
B. Two years
C. Three years
D. Four years
E. Five years
[1] A, B and C only
[2] A, B and D only
[3] B, C and D only
[4] C, D and E only
Correct Answer: 2
Q.40) Match the column:
A. NIEPA
B. NAAC
C. AICTE
D. ICSSR
I. Promotion of quality in technical education
II. to promote research in social sciences
III. Planning and management of education
IV. Accreditation of higher education institutions
[1] A-III B-IV B-II D-I
[2] A-IV B-III C-II D-I
[3] A-III B-IV C-I D-II
[4] A-IV B-II C-I D-III
Correct Answer: 3
Q.41) CBCS provides an opportunity for students to choose courses from:
A. Core courses
B. Environmental education
C. Elective courses
D. Computer courses
E. Ability enhancement courses
[1] A, B and C only
[2] B, C and D only
[3] C, D and E only
[4] A, C and E only
Correct Answer: 4
Q.42) The key objective of RUSA is to improve:
A. Access
B. Equity
C. Quality
D. Infrastructure
E. Curriculum
[1] A, B and C only
[2] B, C and D only
[3] C, D and E only
[4] A, B and E only
Correct Answer: 1
Q.43-47)
Read RC Passage to Answer:
The social structure of most developing countries no longer consists of a tiny upper class confronting a very large and mainly rural lower class, as earlier stereotypes had it. Intermediate strata have grown and diversified until they are, in atleast some respects (recruitment to position of power, control of major political movements) dominant. In almost all of these countries, however, the ‘middle strata’ remain minorities (sometimes very small minorities) and have not achieved sufficient homogeneity of characteristics and interests to entitle them to the label of class.
The key differences between them and the middle classes in the past of the countries that are now industrialised or developed seem to be the following: first, the much greater importance of the role of formal education in giving access to middle (as well as upper) status; second, the much greater importance of salaried employment, particularly in the public sector, in relation to self-employment in the professions or in small businesses; third, the presence of the ‘demonstration effect’ from the high income countries continually tending to stretch consumption aspirations beyond income capacity. Independent, frugal, entrepreneurially minded middle groups can still be identified, and some of them are coping resiliently with economic globalisation and other challenges. However, many factors in the situations in which they have found themselves- technological dependency, the dominance of large-scale enterprises, the bureaucratisation of the rules of the game- generally restricted them to secondary roles in economic evolution. Their educational aspiration for their children have been likely to divert most of these into bureaucratic or professional occupations. Moreover, in many cases, they have belonged to cultural minorities or alien immigrant groups encountering resistance once they become economically conspicuous.
Q.43) The present-day social structure in developing countries is punctuated by
[1] Stereotypical classes
[2] A small group of upper class
[3] A vast mass of rural class
[4] A growing intermediate stratum
Correct Answer: 4
Q.44) In the industrialised countries, people attained the status of the middle class because of access to
[1] Formal education
[2] Employable economic sectors
[3] Areas of self-employment
[4] Special minority tag
Correct Answer: 1
Explanation:
In the industrialised countries, people attained the status of the middle class because of access to formal education. The passage highlights that a key difference between the middle classes in developing countries and those in now-industrialized countries is the “much greater importance of the role of formal education in giving access to middle (as well as upper) status.”
Q.45) What do you understand by ‘demonstration effect’ as mentioned in the passage?
[1] Public sector salaried employment as a goal
[2] Imitation of consumption aspirations of rich counties beyond one’s income
[3] Control of power positions
[4] Mobility from low income group to high income group
Correct Answer: 2
Q.46) Which of the following are the restrictive factors for the development of middle groups?
A. Attitude of independence and frugality
B. Technological dependency
C. Secondary role of bureaucracy
D. Powerful and large business houses
[1] A and B only
[2] B and C only
[3] B and D only
[4] C and D only
Correct Answer: 3
Q.47) The passage is focused on
[1] The secondary roles of economic evolution
[2] The rules of bureaucratisation
[3] The need for economic globalisation
[4] Developmental options of the intermediate strata
Correct Answer: 4
Address
Bani Park, Jaipur, Rajasthan 302016
contact@arpitakarwa.com
Contact
Connect with us




Courses
Quick Links
Don’t waste time browsing several apps. The only app you need for your Exam Preparation is here!